Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT)
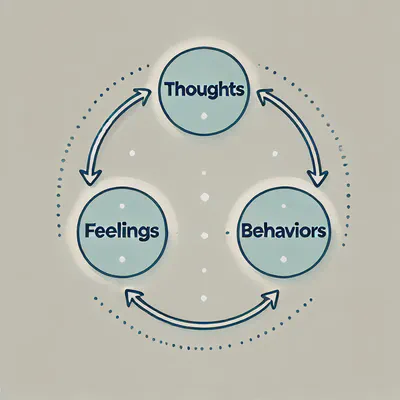
Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT) is a therapeutic approach aimed at identifying and altering negative patterns of thinking and behaviour that contribute to emotional distress. The core idea behind CBT is that thoughts, feelings, and behaviours are interconnected, and that changing negative thought patterns can lead to more positive emotional responses and healthier actions. This therapy is particularly effective because it is highly structured, goal-oriented, and focuses on the present, helping individuals actively work on the issues affecting their mental well-being.
One of the key components of CBT is recognising and challenging distorted or harmful thoughts. People often develop automatic negative thoughts in response to certain situations, which can amplify feelings of anxiety, depression, or stress. CBT helps individuals question the validity of these thoughts, looking for evidence that supports or refutes them. By doing so, individuals can gain a clearer, more balanced perspective and gradually replace negative thinking patterns with more constructive ones. This process not only improves mental clarity but also empowers individuals with practical tools to manage difficult emotions and situations.
CBT is widely used for various mental health concerns, such as anxiety disorders, depression, and stress-related conditions, but it can also be beneficial for managing anger, trauma, and phobias. The structured nature of CBT allows individuals to set specific goals and track their progress, making it easier to see improvements over time. Through CBT, people learn to cope with life’s challenges more effectively by developing healthier thinking patterns and behavioural responses, ultimately fostering a sense of control and resilience in their daily lives.